What is Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) in Healthcare?
“Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)” in healthcare refers to the end-to-end administrative and clinical functions that capture, manage, and collect patient service revenue. It encompasses the entire lifecycle of a patient encounter – from appointment scheduling and registration to final payment or write-off.
It’s critical because even minor inefficiencies at any stage can result in delayed reimbursements, write-offs, compliance risk, or revenue leakage. In a sector where margins are often thin and regulatory scrutiny is high, optimizing RCM is not optional – it’s a financial necessity.
Hospitals and health systems routinely report that 2% to 5% of net patient revenue is lost due to inefficiencies in their RCM operations.
A well-designed RCM system supports cash flow stability, operational transparency, and accountability across clinical, billing, and financial teams.
Why healthcare organizations can’t ignore RCM efficiency
- Revenue leakage is cumulative. Losing 3% here, 2% there – across thousands of claims – becomes millions of dollars lost annually.
- Denials and rework sap labor resources. Each denied or rejected claim must be reworked, appealed, resubmitted – all of which cost time and money.
- Delays hurt cash flow and forecasting. Inconsistent collections make budgeting and capital investment risky.
- Compliance and audit risk. Errors in billing, coding, or documentation invite audits, penalty exposure, or revenue recoupments.
- Patient experience and satisfaction. When billing is opaque or confusing, patients may resist paying. Transparent, timely billing fosters trust and higher collections.
Key Stages of the Revenue Cycle Management Process
The key stages of the revenue cycle management process in healthcare form a structured framework that drives financial accuracy and operational efficiency. Each phase – from patient registration to final collections – plays a vital role in ensuring providers receive proper reimbursement while maintaining compliance and patient satisfaction. Understanding and optimizing every stage of the RCM process helps healthcare organizations reduce denials, accelerate payments, and achieve sustainable revenue growth.
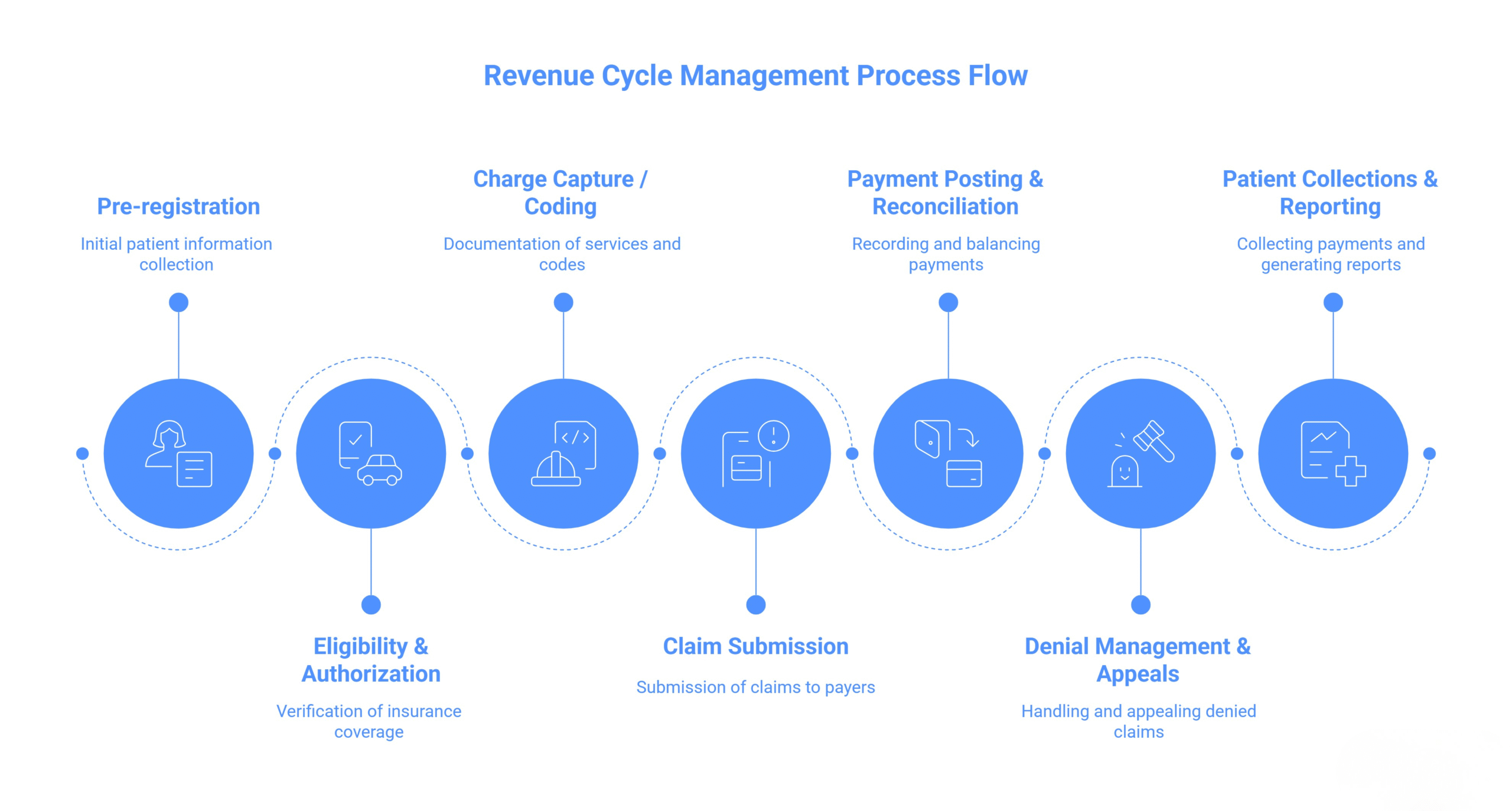
1. Patient Pre-Registration and Eligibility Verification
- At intake or scheduling, capture accurate patient demographics, insurance details, and eligibility.
- Verify coverage, benefit levels, co-pays/deductibles, and any prior authorizations needed.
- Ensure data hygiene (correct names, DOB, insurance IDs) to prevent downstream denials.
- Use real-time eligibility verification systems to flag gaps or lapses before service.
2. Charge Capture and Medical Coding
- Document every service, supply, and procedure delivered in structured form.
- Map clinical documentation (EHR notes) to standardized billing codes (ICD, CPT, HCPCS).
- Use audits and coding validation tools to minimize undercoding, miscoding, or missed charges.
- If charge capture is weak (e.g., manual logs, missing entries), revenue leakage multiplies. (Especially in high-volume or rural settings)
3. Claims Submission
- Assemble clean, scrubbed claims (checking for mandatory fields, formatting, modifiers).
- Route claims electronically per payer guidelines, meeting timely filing windows.
- Apply payer-specific business rules or edits before submission.
- Leverage clearinghouse tools and claim scrubbing to reduce reject/denial risk.
4. Payment Posting and Reconciliation
- Receive remittance advice (ERA/EOB) from payers; post payments and adjustments against claims.
- Identify underpayments, discrepancies, and variances.
- Segregate correct payments vs. partial payments needing follow-up.
- Reconcile to general ledger and flag anomalies for review.
5. Denial Management and Appeals
- Classify denials into soft (fixable) vs hard (final) and triage accordingly.
- Track denial root causes (eligibility, coding, documentation, authorization).
- Perform timely appeals or resubmissions where possible.
- Use denial analytics to identify recurring patterns and feedback for upstream prevention.
- According to industry research, 86 % of denials are potentially avoidable.
- Many organizations see 10–15 % claim denial rates.
6. Patient Collections and Reporting
- Generate patient statements, billing notices, and reminders promptly.
- Offer flexible payment plans, online pay portals, and clear financial counseling.
- Monitor aging accounts receivable (AR), follow up on slow payers, and write off bad debt when necessary.
- Produce dashboards and reports showing trends (e.g., clean claim rate, denial rate, AR days).
The Role of Technology in RCM
1. How automation and AI improve RCM workflows
- Claim scrubbing & edits: Automated checks before submission reduce reject/denial rates.
- Predictive denial analytics: AI models can flag claims with high denial likelihood and prompt preemptive fixes.
- Intelligent routing & bidding: Automate assignment of claims to optimal payer paths.
- Automated appeals workflows: Track and escalate denials based on severity and deadlines.
- Robotic process automation (RPA): Automate repetitive tasks like data extraction, remittance matching, and status inquiries.
2. The impact of EHR integration on financial performance
- Seamless integration between EHR/clinical systems and billing modules prevents transcription errors and delays.
- Real-time capture of charges at point of care ensures accuracy and timeliness.
- Shared data across clinical and financial systems increases visibility and reduces silos.
- Integrated systems support closed-loop feedback (e.g. denial reasons pushing improvements upstream in documentation).
3. Real-time analytics for revenue insights
- Dashboards alert to trends: rising denial clusters, payer lag, underpayment variances.
- Predictive models project cash flow, AR aging, and likely risk exposures.
- Drill-down analytics allow root-cause diagnosis (by payer, department, service).
- Real-time insights empower quicker corrective action and continuous process improvement.
Common Challenges in Revenue Cycle Management
1. Inefficient claims and denial management
- High denial rates (10–15 %) are common and rising.
- Reworking denied claims is expensive (often $25+ per claim) and labor intensive.
- Many denied claims are never appealed—research suggests 65 % of denials go unworked, causing ~3 % net revenue loss.
- Payer complexity: each insurer has distinct business rules, documentation requirements, and denial codes, making consistent compliance difficult.
2. Lack of interoperability between systems
- Disconnected EHRs, billing, and payer systems create data silos and manual handoffs.
- Legacy or homegrown systems often can’t scale or integrate with modern RCM modules.
- Poor data mapping leads to mismatches and errors when transferring between modules.
3. Regulatory changes and compliance burdens
- Frequent updates to coding systems (ICD, CPT, HCPCS) require ongoing training and software updates.
- Payer audits, regulatory reporting, and shifting reimbursement models raise risk.
- Compliance with privacy laws (e.g., HIPAA in the U.S.) adds complexity to data sharing and handling.
4. Staff shortages and training gaps
- Skilled coders, billing experts, and denial analysts are in high demand and low supply.
- Turnover strains continuity, and training new staff is time-consuming.
- Manual processes consume staff bandwidth, leaving little time for higher-value tasks.
5. Inaccurate patient data and eligibility issues
- Incorrect demographic or insurance data at registration causes claim rejections or denials.
- Benefit changes, lapsed coverage, or policy exclusions may go unrecognized.
- Patients may have multiple coverages; coordination-of-benefits errors are frequent.
Proven Solutions to RCM Challenges
1. Centralizing data and improving interoperability
- Migrate to a unified platform where clinical, financial, and payer data reside in shared modules.
- Use APIs and middleware to connect formerly disparate systems.
- Standardize data formats and master patient indexing to eliminate duplication.
- A unified system avoids data handoffs and reduces transcription errors.
2. Leveraging AI-powered automation
- Use AI to predict claim denial risk and trigger alerts for pre-submission remediation.
- Automate denial appeals or routing based on severity thresholds.
- Use natural language processing (NLP) to scan documentation and flag missing elements.
- Automate remittance reconciliation, variance detection, and payment adjustment workflows.
3. Regular staff training and process audits
- Host frequent coding, documentation, and compliance refreshers.
- Perform root-cause audits on denied claims and feed insights upstream.
- Create feedback loops so denials drive changes in registration, documentation, or service workflows.
- Incentivize accuracy and performance (e.g. bonuses, recognition for clean claims).
4. Enhancing patient financial transparency
- Provide cost estimates, pricing tools, and financial counseling before or at service.
- Offer digital statements, online billing portals, and payment plans.
- Communicate clearly about co-pays, deductibles, and balances.
- Transparently assigning patient responsibility reduces disputes and collection friction.
5. Outsourcing or partnering with RCM specialists
- Use third-party RCM vendors or managed services for specialty functions (e.g. denial appeals, AR aging).
- Hybrid models: internal core team + specialist partners for high-skill tasks.
- Many hospitals see ROI from outsourcing non-core, labor-intensive tasks while retaining control of strategy.
- Case study angle: e.g., “A mid-size hospital increased collections by 20 % within 6 months after deploying an AI-augmented RCM partner.”
Metrics to Track for a Healthy Revenue Cycle
To monitor your RCM health, focus on these key performance indicators (KPIs):
| Metric | Why It Matters | Target / Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Days in Accounts Receivable (A/R) | Measures how quickly claims are paid | 30–45 days (varies by payer mix) |
| Clean Claim Rate | Percentage of claims accepted on first pass | ≥ 95 % |
| Denial Rate | Percentage of claims denied initially | < 10 %, ideally < 5 % |
| Net Collection Ratio (NCR) | Actual collections / total expected | ≥ 95 % |
| Patient Payment Turnaround Time | Time from statement to payment | 15–30 days |
| Underpayment / Adjustment Variance | $ or % of claims paid less than billed | < 2–4 % |
| Appeal & Recovery Rate | % of denied claims successfully overturned | ≥ 50–70 % depending on payer |
These metrics should be tracked by payer, service line, department, and denial reason so you can spot trends, diagnose issues, and direct improvement efforts.
Future of Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
1. Predictive analytics for proactive revenue management
- Machine learning models will forecast payer behavior, claim risk, and cash flow scenarios.
- Predictive systems may proactively flag high-risk encounters for additional review or documentation predication.
- Models like “Deep Claim” have shown promise in predicting payer responses with improved recall.
2. The rise of value-based care and its financial impact
- As more providers transition to bundled payments, capitation, or risk-sharing models, RCM must evolve beyond fee-for-service.
- Revenue cycle systems will need to accommodate quality metrics, risk corridors, shared savings, and population health incentives.
- Financial models will shift from volume to value — requiring tighter integration of clinical and financial data.
3. AI-driven coding and claims automation
- AI-assisted coding may push accuracy > 99%, reducing manual effort and audit risk.
- Autonomous claim generation and submission with built-in payer rule logic may emerge.
- Self-learning systems adapt to payer policy changes automatically over time.
4. Patient-centered RCM systems
- RCM systems will cater to the patient journey (financial counseling, price transparency, digital payments).
- Consumerization of healthcare demands billing systems that feel more like e-commerce: intuitive, transparent, flexible.
- Real-time financial estimate tools, chatbot support, and mobile pay are becoming table stakes.
How Curitics Health Simplifies RCM Operations
1. Unified workflows for billing, claims, and reporting
Curitics Health offers a fully unified RCM platform that brings registration, coding, billing, and reporting into a single, seamless interface. No more fragmented modules – all data flows in context, with fewer handoffs and reduced transcription errors.
2. Integrations with EHR and payer systems
Curitics is built with robust API connectors to leading EHRs, payer portals, and clearinghouses. This integration ensures that clinical documentation, insurance verification, and payer responses stay synchronized – reducing delays and manual reconciliation.
3. End-to-end visibility across the revenue lifecycle
With Curitics, revenue cycle managers gain real-time dashboards and analytics at every stage: pre-registration, claims in flight, denials, AR aging, and patient collections. Predictive engines anticipate problem claims and recommend preventive actions.
4. AI-native enhancements and continual learning
Curitics embeds AI modules at key touchpoints:
- Pre-submission scrubbers flag anomalies before claim submission
- Denial risk predictors flag high-risk claims for review
- Auto-appeal engines route and escalate appeals based on severity and payer logic
- Feedback loops update system rules based on actual outcomes
Together, these capabilities help healthcare organizations reduce denials, accelerate collections, and optimize cash flow — all within a unified, intelligent platform.
Conclusion
Revenue Cycle Management in healthcare is more than a back-office function – it’s central to financial viability, operational efficiency, and patient experience. While the RCM journey is complex and fraught with challenges (rising denials, system fragmentation, skilled staffing gaps), the path to improvement is clear:
- Optimize each stage of the revenue cycle with best practices.
- Leverage intelligent automation and AI to reduce manual errors and speed workflows.
- Track the right metrics continuously to identify leaks and drive accountability.
- Adopt unified platforms and interoperability as foundational enablers.
- Prioritize patient transparency — easier billing, clearer payments, better compliance.
Curitics Health is positioned to help healthcare organizations modernize their RCM operations – unifying workflows, applying AI-driven enhancements, and providing end-to-end visibility across the revenue cycle.

No comment yet, add your voice below!